
A Beginner’s Guide to Metal Profile Bending
Profile Bending
Learn the basics of Metal Profile Bending, along with practical tips for achieving precise metal profile bends.
WHAT IS Profile Bending?
Versatile Curves for Industrial and Structural Needs
This 4-minute and 17-second video showcases the roll bending of common metal profiles, and it’s worth watching until the end.
Profile bending is the process of curving metal profiles—such as beams, tubes, channels, and custom extrusions—into precise arcs or complex shapes without compromising structural integrity. It is a critical forming technique used in industries like construction, rail transit, automotive, and aerospace.
At BIT, profile bending includes a wide range of advanced methods:
Roll bending for smooth, continuous curves;
Stretch forming for tight-radius and compound curves;
Rotary draw bending for precision-controlled bends;
Flexible presses and freeforming for custom geometries;
And Fluid Cell and elastoforming presses for high-value, aerospace-grade materials.
These technologies allow us to meet the most demanding requirements in structural performance.
Processes for bending Structurals, Extrusion, Tubes, and Pipe profiles
Profile Bending for All Materials and Industries
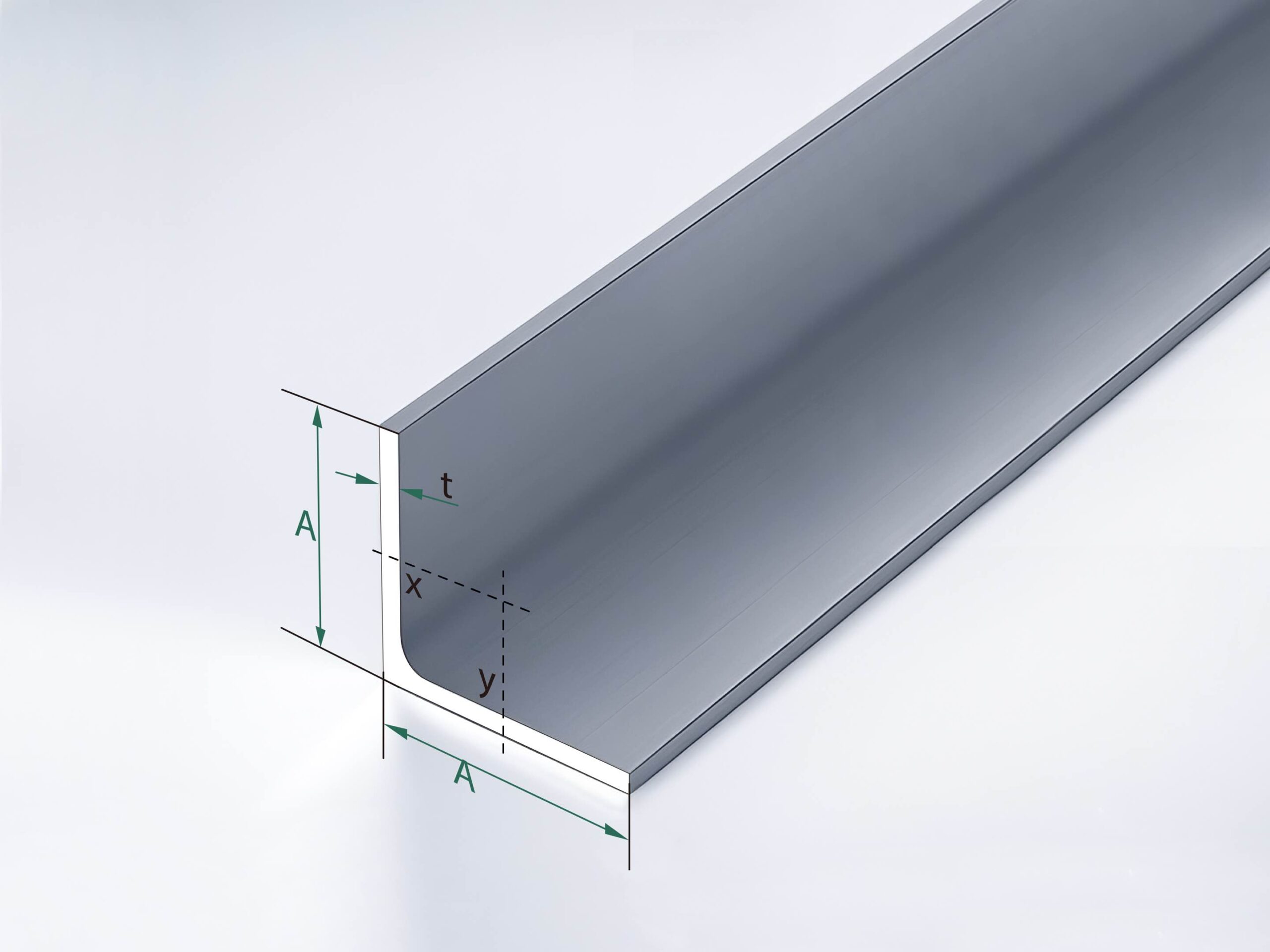
Metal Profile and Section Bending – Steel Profile Bending & Aluminum Profile Bending
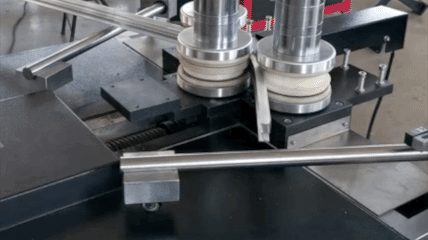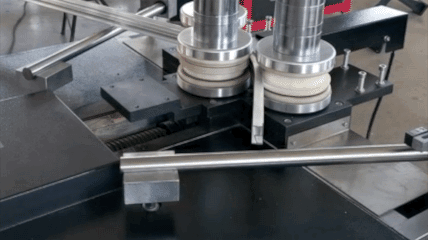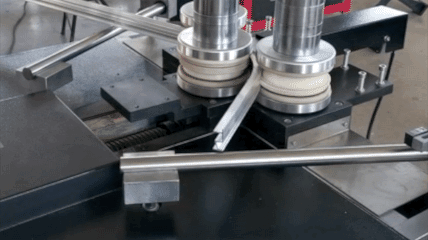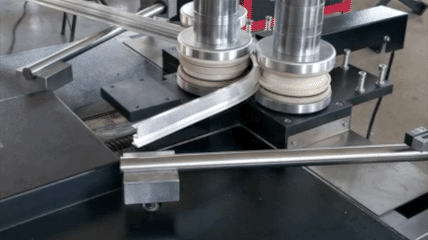
Profile bending(Common Profile and Section Bending includes: angle profile bending, beam profile bending, channel profile bending, pipe profile bending, tube profile bending) actively accommodates a wide range of materials to meet diverse industry needs:
- Steel Profiles: Round Tubes, Square Pipes, Channel Steel, Angle Steel, I-Beams, Flat Bars, Square Bars, T-Sections, and More.
- Stainless Steel: Square Tubes, Round Pipes, Oval Pipes, Special-Shaped Pipes, and Profiles Similar to Carbon Steel.
- Copper Profiles: Busbar, Square Tubes, Round Pipes, Special-Shaped Tubes, Flat Bars, and More.
- Aluminum Profiles: Busbar, Round Pipes, Special-Shaped Tubes, and More Extrusion Profiles
4 Key Knowledges of Profile Bending

- Profile dimensions determine the bending method. For hollow profiles used in curtain walls, when the size exceeds 200mm, roll-bending for strong-axis bending is unsuitable. Stretch forming is recommended instead.
- Bending radius is crucial for steel component bending. Larger radii require roll bending, while stretch forming applies to processes roll bending can’t achieve (3D or a minimum radius less than three times the material width). For smaller radii (greater than 2D), rotational stretching and hot bending are used.
- The terms “Easy way” and “Hard way” refer to bending around the weak or strong axis, respectively, not to the difficulty of bending.
- True HSS material can be helically bent without separating and welding parts. It also doesn’t require filling with other structural components for internal support.
Top 5 Key Quality Requirements for Profile Bending
Guarantees high-quality, reliable, and durable results in profile bending processes.

- Precision: Ensure curvature radius, angle, and length meet specifications. Control deviations within ±1mm or less.
- Deformation: Maintain the cross-section shape, avoiding twisting or warping. Control wall thickness to prevent instability. For hollow profiles, ensure no collapse or deformation.
- Surface: Avoid scratches, dents, cracks, or other damages. Ensure smooth, wrinkle-free surfaces.
- Consistency: Achieve smooth transitions between bent and straight sections. Maintain uniformity in batch production for repeatability.
- Performance: Distribute stress evenly to prevent deformation or cracking. Use suitable molds to reduce residual stress. Preserve wall thickness and mechanical properties.
Applications of Metal Profile Bending

Steel Profile Bending
- Architecture: Roofing, arches, facades, staircases, beams, canopies, and signage.
- Construction: Structural beams, fencing, gates, awnings, and formwork.
- Energy: Refinery parts, heat exchangers, piping systems, and transmission towers.
- Industrial: Conveyor systems, machine frames, storage solutions, and safety barriers.
- Infrastructure: Tunnels, bridges, viaducts, aqueducts, and telecommunication towers.
- Agriculture: Grain silos, greenhouses, water tanks, and livestock handling equipment.
- Transport: Highways, railways, airports, and marine handrails.
- Military: Protective plates, truck water tanks, and machine gun turrets.
Aluminum Profile Bending
- Doors, windows, curtain walls, balcony railings, and handrails.
- Automotive: roof racks, window trims, and crash beams.
- Aerospace parts.Lighting fixtures and illumination components.
- Rail transportation, elevators, and ships.